Pythagorean theorem
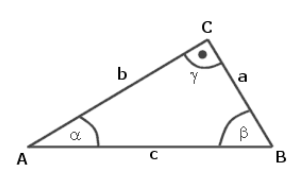
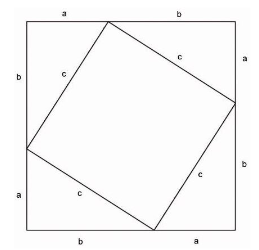
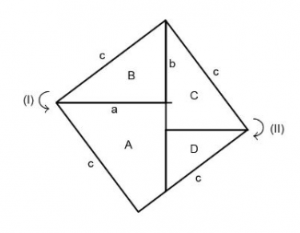
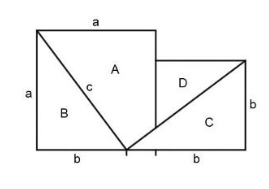
The Pythagorean theorem is one of the fundamental theorems of two-dimensional geometry. It states that for all right-angled triangles (cf. Figure 1) the side lengths are in a certain ratio to each other: If one forms a square over each of the three sides, the sum of the areas of the two smaller squares (over the Cathetes ![]() and
and ![]() ) is exactly as large as the area of the large square (above the hypotenuse
) is exactly as large as the area of the large square (above the hypotenuse ![]() ). Expressed as an equation, the Pythagorean theorem is therefore simply
). Expressed as an equation, the Pythagorean theorem is therefore simply ![]() .
.